What Do Dental Implants Look Like?
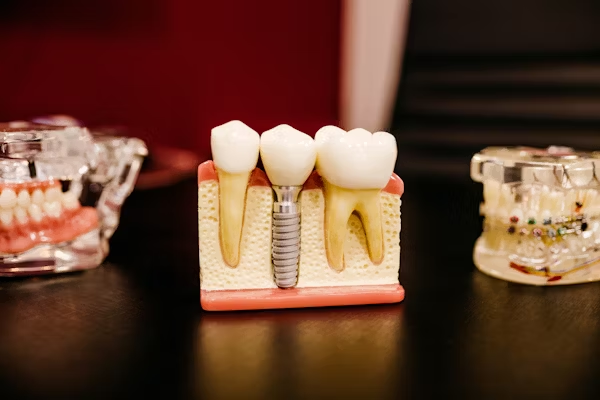
If you’re considering dental implants, it’s natural to wonder: What do dental implants actually look like? The idea of replacing a tooth can feel technical or even intimidating at first—but modern implant design is remarkably refined.
Today’s implants are engineered to mimic the appearance and function of natural teeth so closely that most people will never notice the difference. With advancements in cosmetic dentistry and digital technology, especially at leading practices at The Tooth Co. in Irvine, CA, patients can expect results that are aesthetic, durable, and exceptionally lifelike.
This guide takes you through every visual aspect of dental implants—from the hidden implant post to the crown you’ll see when you smile—so you know exactly what to expect.
What Do Dental Implants Look Like
Dental implants are created to replicate the look and feel of natural teeth with remarkable precision. From the shade of the crown to the shape of the gumline, each detail is customized so closely that the final result blends seamlessly into your smile.
What Are Dental Implants?
Dental implants are permanent tooth replacements composed of three key components. Each part plays an essential role in creating a natural-looking restoration.
The Three-Part Structure
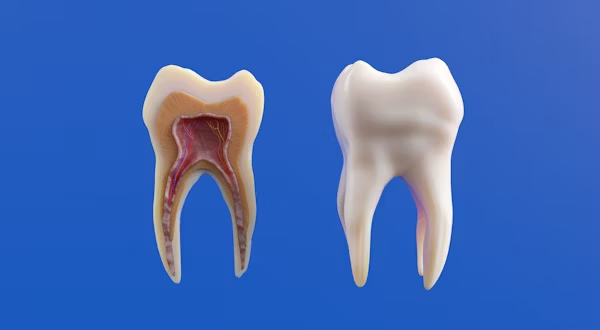
Implant Post
A biocompatible screw-like root placed within the jawbone.
Abutment
A connector that attaches the crown to the implant post.
Crown
The visible part of the implant—shaped and shaded to resemble a natural tooth.
How Implants Replicate Natural Teeth
Because implants replace both the root and the visible tooth structure, they replicate the full anatomy of natural teeth, allowing for exceptional stability and aesthetics.
What the Implant Post Looks Like
The implant post is never visible in your mouth, but its design plays a major role in long-term stability.
Titanium and Zirconia Materials
Titanium posts appear metallic silver, while zirconia posts are tooth-colored ceramic options.
Shape and Size of the Implant Screw
They resemble tiny, tapered bolts with threads that allow them to integrate with bone.
Why the Implant Post Is Not Visible Once Placed
It is fully concealed beneath the gum tissue and bone after healing.
What the Abutment Looks Like
Connector Between the Implant and Crown
A small extension piece that sits above the gumline before the final crown is placed.
Materials and Color Choices
- Titanium
- Zirconia
- Gold (rarely used today)
When the Abutment Is Visible and When It’s Not
It may be visible briefly during healing but disappears once the permanent crown is attached.
What the Implant Crown Looks Like
Porcelain or Ceramic Tooth-Like Appearance
Crown materials are designed to reflect light like natural enamel.
Shade Matching to Surrounding Teeth
Dentists match color, brightness, and translucency to neighboring teeth.
Shape Customization for Natural Fit
The crown is crafted to mimic the natural tooth it replaces.
How Dental Implants Look Compared to Natural Teeth
Color Similarities
Advanced shading techniques allow an almost perfect match.
Texture and Light Reflection
Ceramic crowns imitate enamel texture and gloss.
Alignment and Contour Matching
Implants are positioned to mirror the alignment of natural teeth.
Dental Implants vs. Dentures and Bridges (Appearance)
Natural Look Advantages
Implants emerge from the gums like real teeth.
Gumline Aesthetic Differences
Unlike dentures, implants don’t show acrylic gums.
Stability and Visual Integration
Implants remain fixed—no shifting or visible movement.
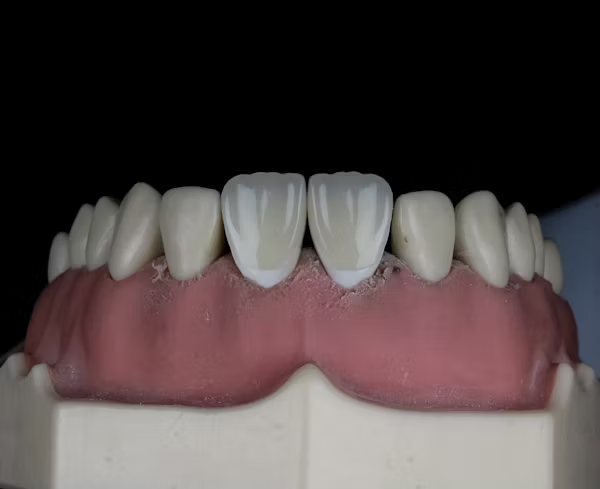
What Single Implants Look Like
Replacement of a Single Missing Tooth
Designed to blend effortlessly with surrounding teeth.
How It Blends Into a Full Smile
Careful color and contour matching ensures it doesn’t stand out.
Close-Up Appearance Differences
Even close-up, high-quality crowns look very natural.
What Multiple Implants Look Like
Side-by-Side Restorations
Multiple implants create a uniform, cohesive appearance.
Matching Color and Shape Across Several Teeth
Digital dentistry helps achieve perfect symmetry.
Implant Bridges and Their Aesthetic Features
Implant-supported bridges look more natural than traditional bridges due to improved stability.
What Full Mouth Implant Systems Look Like
All-on-4 and All-on-6 Implant Aesthetics
Full-arch systems support complete sets of teeth that look symmetrical and natural.
How Full Arch Restorations Mimic Natural Teeth
The teeth are crafted to resemble real enamel, while gum-colored components mimic healthy tissue.
Gum-Colored Components in Full Arch Implants
These help recreate natural gum contours for improved aesthetics.
How the Gumline Looks With Implants
Pink Porcelain or Composite Gum Replication
Used when artificial gum material is needed for aesthetics.
Natural Tissue Contouring
Dentists sculpt the tissue around the crown for a seamless blend.
Avoiding Gaps and Dark Shadows
Correct positioning prevents shadowing or open spaces.
X-Ray Appearance of Dental Implants
What Dentists See During Evaluation
Implants appear brighter and more defined than natural bone.
How Implants Look Beneath the Bone
They show as securely integrated, screw-shaped structures.
Why X-Ray Differences Are Not Visible in Real Life
The visible crown hides all internal components.
Temporary Implants and Healing Caps
What Temporary Crowns Look Like
Made of resin, these provide a simple but natural appearance during healing.
Appearance During Healing Period
Slightly less detailed than the final restoration but cosmetically acceptable.
Differences Between Temporary and Final Restorations
Final crowns offer superior shape, polish, and translucency.
How Implants Look Over Time
Maintaining Color Stability
Implant crowns resist staining better than natural teeth.
Wear Resistance of Implant Crowns
Ceramic materials hold their shape extremely well.
Gum Health and Long-Term Aesthetics
Healthy gums maintain the implant’s seamless appearance.
Implant Aesthetics for Front Teeth
Challenges in the “Smile Zone”
Front teeth require precise shading and symmetry.
Importance of Shade, Shape, and Translucency
Front implants must mimic natural enamel more closely.
Achieving Symmetry With Natural Teeth
Digital design ensures balance and proportion.
Implant Aesthetics for Back Teeth
Strength Over Aesthetic Focus
Molars prioritize durability more than cosmetic detail.
How Molars Are Designed Differently
They mimic the larger, grooved structure of natural molars.
Why Back Implants Are Less Visible
They sit in the less prominent area of your mouth.
Factors That Affect How Implants Look
Bone Density and Placement Angle
Good bone support ensures correct implant positioning.
Gum Thickness and Tissue Health
Thicker gums create a more natural appearance.
Dentist Technique and Crown Design
Skill and precision significantly influence the final look.
How Digital Dentistry Improves Implant Appearance
3D Scanning
Offers highly detailed imaging.
CAD/CAM Custom Crown Design
Allows exact customization.
Precision Fit for Natural Results
Ensures a comfortable, seamless integration.
Comparing Implant Crowns to Real Enamel
Light Reflection and Gloss
Ceramics are layered to mimic the shine of natural teeth.
Color Layering Techniques
Multiple layers add depth and realism.
Matching Natural Variations in Tooth Shades
Even subtle imperfections can be replicated.
Common Concerns About Implant Appearance
Will the Implant Post Show?
No, it remains hidden beneath gum and bone.
Will the Color Match My Other Teeth?
Yes—the shade is carefully selected for accuracy.
Can People Tell I Have an Implant?
With modern materials, implants look incredibly natural.
Caring for the Look of Your Dental Implants
Preventing Stains on Implant Crowns
Limit exposure to deep-colored foods and drinks.
Daily Cleaning to Maintain Shine
Brush, floss, and schedule regular dental cleanings at The Tooth Co..
Protecting the Gumline Around Implants
Healthy gums help maintain aesthetic harmony.
When Implant Aesthetics May Need Adjustment
Crown Replacement After Many Years
Occasionally needed to refresh appearance.
Gum Recession Management
Treatment can restore natural-looking gum contours.
Improving Color Match With Updated Materials
Newer ceramics offer enhanced realism.
The Tooth Co.: Experts in Natural-Looking Dental Implants
Located at 114 Pacifica, Ste 310, Irvine, CA 92618, The Tooth Co. stands out as your premier modern dental studio using advanced digital and clinical techniques. Under the leadership of Dr. Perrin—valedictorian, researcher, and visionary—our practice offers you concierge-level care and stunningly natural implant restorations.
Our patients trust us for exceptional dental services such as digital smile simulations, same-day 3D-printed "Test Drive" veneers, hand-made or 3D-printed veneers, clear aligner therapy, and general dentistry, including implants, crowns, and inlays. Our business hours are Monday from 9 AM–6 PM, Tuesday and Wednesday from 8 AM–5 PM, Thursday from 7 AM–4 PM, and Friday from 8 AM–12 PM, with Saturday appointments available by request.
If you’re seeking the most natural-looking dental implants in Irvine, The Tooth Co. delivers you the ideal blend of technology, precision, and artistry. Contact us today.
Conclusion
Dental implants at The Tooth Co. are designed to look incredibly natural, from the shape of the crown to the contour of the gumline. With the right dentist, advanced digital techniques, and high-quality materials, implants can blend seamlessly into your smile for decades.
Whether you need a single replacement or a full-arch restoration, understanding how implants look helps you feel confident about your treatment journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do implants look fake?
High-quality implants are crafted to look nearly identical to natural teeth.
Can implants be made whiter than natural teeth?
Yes—your dentist can design a crown in your preferred shade.
Will my gums look natural around the implant?
With proper contouring, gum tissue blends smoothly around your new crown.
How does The Tooth Co. ensure natural aesthetics?
Through digital imaging, expert craftsmanship, and advanced shading techniques.